Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Ni and
Ni and  Zr at 0.4, 1.3, 2.2, and 3.0 GeV
Zr at 0.4, 1.3, 2.2, and 3.0 GeVTakeshita, Hayato*; Meigo, Shinichiro; Matsuda, Hiroki*; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Nakano, Keita; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Maekawa, Fujio
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 527, p.17 - 27, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:50.96(Instruments & Instrumentation)To improve accuracy of nuclear design of accelerator driven nuclear transmutation systems and so on, nuclide production cross sections on Ni and Zr were measured for GeV energy protons. The measured results were compared with PHITS calculations, JENDL/HE-2007 and so on.
 Lu target irradiated with 0.4-, 1.3-, 2.2-, and 3.0-GeV protons
Lu target irradiated with 0.4-, 1.3-, 2.2-, and 3.0-GeV protonsTakeshita, Hayato; Meigo, Shinichiro; Matsuda, Hiroki; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Nakano, Keita; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Maekawa, Fujio
JAEA-Conf 2021-001, p.207 - 212, 2022/03
Prediction of nuclide production of spallation products by high-energy proton injection plays a fundamental and important role in shielding design of high-intensity proton accelerator facilities such as accelerator driven nuclear transmutation system (ADS). Since the prediction accuracy of the nuclear reaction models used in the production quantity prediction simulation is insufficient, it is necessary to improve the nuclear reaction models. We have measured nuclide production cross sections for various target materials with the aim of acquiring experimental data and improving nuclear reaction models. In this study, 1.3-, 2.2- and 3.0-GeV proton beams were irradiated to  Lu target, and nuclide production cross-section data were acquired by the activation method. The measured data were compared with several nuclear reaction models used in Monte Carlo particle transport calculation codes to grasp the current prediction accuracy and to study how the nuclear reaction model could be improved.
Lu target, and nuclide production cross-section data were acquired by the activation method. The measured data were compared with several nuclear reaction models used in Monte Carlo particle transport calculation codes to grasp the current prediction accuracy and to study how the nuclear reaction model could be improved.
Takeshita, Hayato; Meigo, Shinichiro; Matsuda, Hiroki; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Maekawa, Fujio; Watanabe, Yukinobu*
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011045_1 - 011045_6, 2021/03
To improve accuracy of nuclear design of accelerator driven nuclear transmutation systems, nuclide production cross sections on Ni and Zr, which were candidate materials to be used in ADS, were measured for GeV energy protons. The measured results were compared with PHITS calculations and JENDL/HE-2007.
Aritomo, Yoshihiro*; Amano, Shota*; Okubayashi, Mizuki*; Yanagi, Baku*; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Ota, Masahisa*
Physics of Atomic Nuclei, 83(4), p.545 - 549, 2020/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Physics, Nuclear)Matsuda, Hiroki; Meigo, Shinichiro; Iwamoto, Hiroki
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 55(8), p.955 - 961, 2018/08
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:45.59(Nuclear Science & Technology)We have started an experimental program to measure activation cross sections systematically in the proton-induced spallation reaction in structural materials commonly used in high-intensity proton accelerator-based facilities, such as Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC). As the first step of the program, aluminum (Al) was chosen to verify the adequacy of the measurement technique implemented in a J-PARC proton beam environment because data of Al have been relatively well studied both by experimental measurement and simulation. Activation cross sections of  Be,
Be,  Na, and
Na, and  Na in Al were measured at proton energy points from 0.4, 1.3, 2.2 to 3.0 GeV, which could be delivered smoothly from the synchrotron. The validity of experimental data has been verified by introducing an effective proton numbers determination procedure. We compared the measured data with existing experimental data, the evaluated data (JENDL-HE/2007), and the calculations with several intra-nuclear cascade models by the Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS) code. Although the experimental data agreed with JENDL-HE/2007, the calculations underestimated about 40%. This could come from the evaporation model (generalized evaporation model) being implemented in the PHITS code. We found that the calculations agreed with the experimental data by an upgraded PHITS code.
Na in Al were measured at proton energy points from 0.4, 1.3, 2.2 to 3.0 GeV, which could be delivered smoothly from the synchrotron. The validity of experimental data has been verified by introducing an effective proton numbers determination procedure. We compared the measured data with existing experimental data, the evaluated data (JENDL-HE/2007), and the calculations with several intra-nuclear cascade models by the Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS) code. Although the experimental data agreed with JENDL-HE/2007, the calculations underestimated about 40%. This could come from the evaporation model (generalized evaporation model) being implemented in the PHITS code. We found that the calculations agreed with the experimental data by an upgraded PHITS code.
Matsuda, Hiroki; Meigo, Shinichiro; Iwamoto, Hiroki
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 1021(1), p.012017_1 - 012017_4, 2018/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.11(Nuclear Science & Technology)Spallation neutron at 180 degrees is of important for an evaluation of radiation protection for ADS (Accelerator-Driven System) and the nuclear physics. It was, however, quite difficult to measure it. We measured the energy spectrum of spallation neutron at 180 degrees at the proton transport beam line (3NBT) to MLF (Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility) on J-PARC by the NE213 liquid scintillator. The irradiated proton energy was 3 GeV, and the intensity was 1 10
10 protons above. The neutron energy was determined by Time-Of-Flight method with n-gamma discrimination. We also simulated the energy spectrum by using PHITS code and compared with measured spectrum. In this paper, the overview of the experiment and the results are described.
protons above. The neutron energy was determined by Time-Of-Flight method with n-gamma discrimination. We also simulated the energy spectrum by using PHITS code and compared with measured spectrum. In this paper, the overview of the experiment and the results are described.
Takada, Hiroshi; Haga, Katsuhiro; Teshigawara, Makoto; Aso, Tomokazu; Meigo, Shinichiro; Kogawa, Hiroyuki; Naoe, Takashi; Wakui, Takashi; Oi, Motoki; Harada, Masahide; et al.
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 1(2), p.8_1 - 8_26, 2017/09
At the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC), a pulsed spallation neutron source provides neutrons with high intensity and narrow pulse width to promote researches on a variety of science in the Materials and life science experimental facility. It was designed to be driven by the proton beam with an energy of 3 GeV, a power of 1 MW at a repetition rate of 25 Hz, that is world's highest power level. A mercury target and three types of liquid para-hydrogen moderators are core components of the spallation neutron source. It is still on the way towards the goal to accomplish the operation with a 1 MW proton beam. In this paper, distinctive features of the target-moderator-reflector system of the pulsed spallation neutron source are reviewed.
Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Kamiya, Junichiro; Watanabe, Masao; Yamazaki, Yoshishige; Irie, Yoshiro; Kishiro, Junichi; Sakai, Izumi*; Kawakubo, Toshimichi*
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 16(2), p.1358 - 1361, 2006/06
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:60.87(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)The injection bump system of the 3-GeV RCS in J-PARC consists of the pulse bending magnets for the injection bump orbit, which are four horizontal bending magnets (shift bump), four horizontal painting magnets (h-paint bump), and two vertical painting magnets (v-paint bump). In this paper, the design of the magnets and power supply of the injection bump system are reported.
Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Kamiya, Junichiro; Watanabe, Masao; Ueno, Tomoaki*; Yamazaki, Yoshishige; Irie, Yoshiro; Kishiro, Junichi; Sakai, Izumi*; Kawakubo, Toshimichi*; Tounosu, Shigeki*; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 16(2), p.1366 - 1369, 2006/06
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:43.72(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)The injection system of the 3-GeV RCS in J-PARC is composed of four main orbit bump magnets (shift bump) to merge the injection beam with the circulating beam. The magnetic field design and the structural analysis of the shift bump magnets have been performed using 3D magnetic and mechanical codes. In this paper, the design of the bending magnets is reported.
Meigo, Shinichiro; Shigyo, Nobuhiro*; Iga, Kiminori*; Iwamoto, Yosuke*; Kitsuki, Hirohiko*; Ishibashi, Kenji*; Maehata, Keisuke*; Arima, Hidehiko*; Nakamoto, Tatsushi*; Numajiri, Masaharu*
AIP Conference Proceedings 769, p.1513 - 1516, 2005/05
For validation of calculation codes that are employed in the design of accelerator facilities, spectra of neutrons produced from a thick iron target bombarded with 1.5-GeV protons were measured. The calculated results with NMTC/JAM were compared with the present experimental results. It is found the NMTC/JAM generally shows in good agreement with experiment. Furthermore, the calculation gives good agreement with the experiment for the energy region 20 to 80 MeV, whereas the NMTC/JAM gives 50 % of the experimental data for the heavy nuclide target such as lead and tungsten target.
Maekawa, Fujio; Meigo, Shinichiro; Kasugai, Yoshimi; Takada, Hiroshi; Ino, Takashi*; Sato, Setsuo*; Jerde, E.*; Glasgow, D.*; Niita, Koji*; Nakashima, Hiroshi; et al.
Nuclear Science and Engineering, 150(1), p.99 - 108, 2005/05
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:40.41(Nuclear Science & Technology)A neutronic benchmark experiment on a simulated spallation neutron target assembly with 1.94, 12 and 24 GeV proton beams conducted by using the AGS accelerator at BNL/US was analyzed to investigate validity of neutronics calculations on proton accelerator driven spallation neutron sources. Monte Carlo particle transport calculation codes NMTC/JAM, MCNPX and MCNP-4A with associated cross section data in JENDL and LA-150 were used for the analysis. As a result, although the overall energy range was encompassed from GeV to meV, i.e., more than 12 orders of magnitude, calculated fast and thermal neutron fluxes agreed approximately within  40 % with the experiments. Accordingly, it was concluded that neutronics calculations with these codes and cross section data were adequate for estimating nuclear properties in spallation neutron sources.
40 % with the experiments. Accordingly, it was concluded that neutronics calculations with these codes and cross section data were adequate for estimating nuclear properties in spallation neutron sources.
Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Irie, Yoshiro; Kamiya, Junichiro; Watanabe, Masao; Watanabe, Yasuhiro; Ueno, Tomoaki*; Noda, Fumiaki*; Saha, P. K.; Sakai, Izumi*; Kawakubo, Toshimichi*
Proceedings of 2005 Particle Accelerator Conference (PAC '05) (CD-ROM), p.1048 - 1050, 2005/00
The pulse bending magnets for the injection system of the 3-GeV RCS in J-PARC has been designed. The injection system consists of the pulsed bending magnets, which are four horizontal bending magnets (shift bump) and four horizontal painting magnets (h-paint bump) for the injection bump orbit, and two vertical painting magnets (v-paint magnet). The injection beam energy and the extraction beam power are 400 MeV and 1 MW at 25 Hz repetition rate, respectively. The acceptance to include the injection beam, the painting beam and the circulating beam at the shift bump points is a 388 mm wide and a 242 mm high. The shift bump has been designed using a 3D magnetic analysis code, which accomplished less than 0.4 % field deviation under 0.26 T excitation level.
Nakashima, Hiroshi; Takada, Hiroshi; Kasugai, Yoshimi; Meigo, Shinichiro; Maekawa, Fujio; Kai, Tetsuya; Konno, Chikara; Ikeda, Yujiro; Oyama, Yukio; Watanabe, Noboru; et al.
Proceedings of 6th Meeting of the Task Force on Shielding Aspects of Accelerators, Targets and Irradiation Facilities (SATIF-6), (OECD/NEA No.3828), p.27 - 36, 2004/00
no abstracts in English
Irie, Yoshiro
Proceedings of 9th European Particle Accelerator Conference (EPAC 2004), p.113 - 117, 2004/00
The MW proton source using rapid cycling synchrotron (RCS) has many challenging aspects, such as (1) large aperture magnets and much higher RF voltages per turn due to a low energy injection and a large and rapid swing of the magnetic field, (2) field tracking between many magnet-families under slightly saturated conditions, (3) RF trapping with fundamental and higher harmonic cavities, (4) H- charge stripping foil, (5) large acceptance injection and extraction straights, (6) beam loss collection, and (7) beam instabilities. These are discussed in details mainly on the basis of the J-PARC 3GeV RCS, which is under construction in Japan. Issues (3) to (7) are common with another scheme of MW spallation neutron source, i.e. full-energy linac + accumulator ring. Comparisons with the SNS design in the US are then made. Reliability/availability of these machines is very important theme which finally determines the successful operations. From the experiences in the existing machines, we will discuss the factors necessary toward the better performance.
Iwase, Akihiro; Hamatani, Yutaro*; Mukumoto, Yoshinori*; Ishikawa, Norito; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Kambara, Tadashi*; M ller, C.*; Neumann, R.*; Ono, Fumihisa*
ller, C.*; Neumann, R.*; Ono, Fumihisa*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 209(1-4), p.323 - 328, 2003/08
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:77.16(Instruments & Instrumentation)Fe=Ni Invar alloy is irradiated with GeV Xe and U ions at room temperature. By the irradiation, the Curie temperature of the soecimens increases, which is correlated with the electronic stopping power. This phenomenon can be explained as due to the lattice expansion and/or the local increase in Ni concentration.
Kai, Tetsuya; Maekawa, Fujio; Kasugai, Yoshimi; Niita, Koji*; Takada, Hiroshi; Meigo, Shinichiro; Ikeda, Yujiro
Proceedings of ICANS-XVI, Volume 3, p.1041 - 1049, 2003/07
A radioactivity calculation code system DCHAIN-SP was validated in view of the following points: (1) Activation cross section data library for the energy region below 20 MeV. (2) NMTC/JAM code for calculation of the nuclide yield induced by the high energy particles above 20 MeV. (3) DCHAIN-SP code system which treats overall nuclide yield by the high energy particles. 42 of activation cross sections and 22 tritium production cross sections were revised so that the DCHAIN-SP calculation could improve its accuracy within 30% for typical materials irradiated by 14-MeV neutrons. The NMTC/JAM code was improved to implement the GEM model for better estimation of light fragment production. Accuracy of the nuclide yield for proton induced reactions in 10 MeV - 10 GeV still remains in the level of a factor of 2 to 3. The DCHAIN-SP code system was employed for the analysis of time evolution of the radioactivity produced in the samples on a thick mercury target bombarded with 2.83 and 24 GeV protons. It is found that the code system agrees with the measured data by a factor of 2 to 3.
Iwase, Akihiro; Hasegawa, Tadayuki*; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Tobita, Toru; Ishikawa, Norito; Suzuki, Masahide; Kambara, Tadashi*; Ishino, Shiori*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 195(3-4), p.309 - 314, 2002/10
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:60.73(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Sasamoto, Nobuo; Nakashima, Hiroshi; Hirayama, Hideo*; Shibata, Tokushi*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 39(Suppl.2), p.1264 - 1267, 2002/08
no abstracts in English
Nakashima, Hiroshi; Takada, Hiroshi; Kasugai, Yoshimi; Meigo, Shinichiro; Maekawa, Fujio; Kai, Tetsuya; Konno, Chikara; Ikeda, Yujiro; Oyama, Yukio; Watanabe, Noboru; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 39(Suppl.2), p.1155 - 1160, 2002/08
no abstracts in English
 Sr
Sr CaCu
CaCu O
O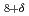 irradiated with GeV heavy ions
irradiated with GeV heavy ionsKuroda, N.; Ishikawa, Norito; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Iwase, Akihiro; Ikeda, Hiroshi*; Yoshizaki, Ryozo*; Kambara, Tadashi*
Physical Review B, 63(22), p.224502_1 - 224502_5, 2001/06
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:47.99(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English